I find the connection between the pituitary gland and testosterone levels to be quite vital for understanding hormonal regulation. The pituitary gland, particularly its anterior lobe, produces luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which are essential for stimulating testosterone production in the testes. This process operates through a feedback loop where elevated testosterone levels signal the pituitary to reduce LH and FSH secretion. Dysfunction in the pituitary can lead to imbalances and decreased testosterone levels, affecting many bodily functions. There's much more to explore about the implications of these dynamics on overall health and treatments available.
Overview of the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the "master gland" of the endocrine system, plays a crucial role in regulating various hormonal functions in the body. Its significance lies in its ability to control multiple glandular activities through hormone secretion, impacting overall glandular health. Located at the base of the brain, this pea-sized gland produces essential hormones that influence growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes.
Understanding pituitary function is fundamental for grasping how hormonal balance is achieved. The pituitary gland is divided into two main parts: the anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior lobe releases hormones such as growth hormone (GH), prolactin, and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are critical for different physiological processes. The posterior lobe, on the other hand, stores and releases oxytocin and vasopressin, which play roles in social behaviors and fluid balance.
To maintain ideal glandular health, the pituitary gland must communicate effectively with other endocrine organs, such as the adrenal glands and thyroid. Any dysfunction in the pituitary can lead to an array of health issues, including hormonal imbalances and metabolic disorders. For instance, overproduction or underproduction of specific hormones can disrupt bodily functions, leading to conditions such as Cushing's disease or hypothyroidism.
Role of Testosterone in the Body
Testosterone serves a significant role in various physiological processes beyond just reproductive health. As I explore deeper into its functions, I realize testosterone's influence extends to muscle mass, bone density, and even cognitive function. It's fascinating to note that testosterone benefits include promoting protein synthesis, which is essential for muscle development and repair. This anabolic effect not only aids in physical strength but also contributes to overall liveliness.
Moreover, testosterone plays an important role in maintaining bone density. Insufficient levels can lead to osteoporosis, making bones more fragile and susceptible to fractures. I find it alarming how testosterone deficiency can compromise this fundamental aspect of health, particularly in aging populations.
Additionally, testosterone impacts mood and cognitive abilities. Low levels can result in mood swings, fatigue, and even depression. It's like a domino effect; when testosterone levels dip, various bodily functions start to falter. I've come to appreciate how this hormone acts as a key modulator in energy levels and mental clarity.
When I consider the thorough role of testosterone, it becomes clear that its deficiency can have far-reaching consequences. Addressing low testosterone levels isn't just about improving libido or reproductive functions; it's about enhancing overall quality of life. Recognizing the multifaceted benefits of testosterone helps underscore the importance of monitoring and maintaining ideal levels for long-term health and well-being.
Hormonal Regulation Mechanism
In this section, I'll explain how the pituitary gland orchestrates the hormone release process that regulates testosterone levels. I'll also examine the feedback loop dynamics that guarantee hormonal balance within the body. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for grasping how testosterone levels are maintained and adjusted.
Hormone Release Process
Hormone release is a complex, tightly regulated process that involves intricate communication between the pituitary gland and other endocrine organs. I often find it fascinating how glandular signaling orchestrates this delicate balance. The pituitary gland, often referred to as the "master gland," synthesizes and releases hormones that directly influence the functioning of other glands, including the testes, which produce testosterone.
Here's a simplified overview of the hormone release process:
| Step | Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Hormone Synthesis | The pituitary synthesizes hormones (e.g., LH) | Stimulates target glands |
| 2. Hormone Release | Hormones are released into circulation | Effects on various organs |
| 3. Target Activation | Hormones bind to receptors on target glands | Initiates physiological response |
| 4. Feedback Mechanism | Signals from target organs regulate release | Maintains homeostasis |
This process is crucial for ensuring that testosterone levels remain within a healthy range. Each step relies on precise signaling pathways, emphasizing the importance of the pituitary gland in overall hormonal regulation and the synthesis of essential hormones like testosterone.
Feedback Loop Dynamics
Throughout the endocrine system, feedback loops play a critical role in regulating hormone levels, guaranteeing that they remain within ideal ranges. These loops primarily involve neuroendocrine interactions, where the hypothalamus and pituitary gland communicate to modulate testosterone production. When testosterone levels rise, they signal the hypothalamus to reduce the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Consequently, this decrease in GnRH results in lower luteinizing hormone (LH) levels from the pituitary gland, ultimately leading to reduced testosterone synthesis in the testes.
Conversely, when testosterone levels drop, the hypothalamus increases GnRH release, prompting the pituitary to secrete more LH. This positive feedback loop guarantees that testosterone levels are adjusted according to the body's needs. The intricacies of this process are underscored by signal transduction pathways, which facilitate the transmission of hormonal signals to target cells, allowing for precise cellular responses.
Pituitary Gland Hormones
In understanding testosterone production, it's essential to examine the hormones produced by the pituitary gland. Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays an important role in stimulating testosterone synthesis, while follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) contributes to the regulation of spermatogenesis. By analyzing these hormones, we can better grasp their impact on testosterone levels and overall reproductive health.
Hormones Regulating Testosterone Production
Testosterone production is primarily regulated by two key hormones secreted by the pituitary gland: luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones play a significant role in testosterone synthesis through complex hormonal interactions. LH stimulates the Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone, while FSH supports the Sertoli cells, which are essential for spermatogenesis and also indirectly influence testosterone levels.
Here's a breakdown of the functions of these hormones:
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| LH | Stimulates testosterone production in Leydig cells |
| FSH | Supports Sertoli cells and indirectly influences testosterone synthesis |
The balance between LH and FSH is important. An increase in LH often correlates with elevated testosterone levels, whereas FSH aids in the maintenance of the environment necessary for effective testosterone synthesis. Disruptions in these hormonal interactions can lead to imbalances in testosterone levels, impacting overall health. Understanding the roles of LH and FSH can provide insight into the intricate regulation of testosterone production and its significance in male reproductive health.
Role of Luteinizing Hormone
The role of luteinizing hormone (LH) in testosterone production is fundamental, as it directly influences the function of Leydig cells in the testes. When the pituitary gland releases LH, it binds to specific receptors on Leydig cells, triggering a cascade of biochemical reactions that enhance testosterone synthesis. This intricate mechanism underscores the significant luteinizing hormone functions in male reproductive health.
Moreover, the regulation of luteinizing hormone levels is essential for maintaining ideal testosterone production. Elevated LH levels often indicate a compensatory response to low testosterone, while low LH levels can signify various health issues, including pituitary dysfunction. It's fascinating how the balance of these hormones can affect overall hormonal homeostasis, impacting not only reproductive functions but also muscle mass, mood, and energy levels.
In my analysis, understanding the relationship between LH and testosterone is critical for diagnosing and treating conditions like hypogonadism or infertility. By monitoring luteinizing hormone levels, healthcare professionals can better tailor interventions aimed at restoring hormonal balance. Essentially, LH serves as a key regulatory hormone, bridging the communication between the pituitary gland and the testes, thereby influencing testosterone levels and overall male health.
Impact of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
Understanding the impact of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) on male reproductive health is fundamental. FSH, produced by the anterior pituitary gland, plays a significant role in regulating spermatogenesis and influences testosterone levels indirectly. By stimulating Sertoli cells in the testes, FSH facilitates the maturation of sperm cells, which is essential for male fertility.
Here's a concise breakdown of FSH functions and its relationship with testosterone:
| FSH Functions | Impact on Testosterone |
|---|---|
| Stimulates Sertoli cells | Supports Leydig cell function |
| Promotes spermatogenesis | Indirectly enhances testosterone production |
| Regulates testosterone receptors | Increases testosterone sensitivity |
| Influences fluid secretion | Maintains prime environment for sperm |
| Works synergistically with LH | Maximizes overall reproductive hormone balance |
Testosterone Production Process
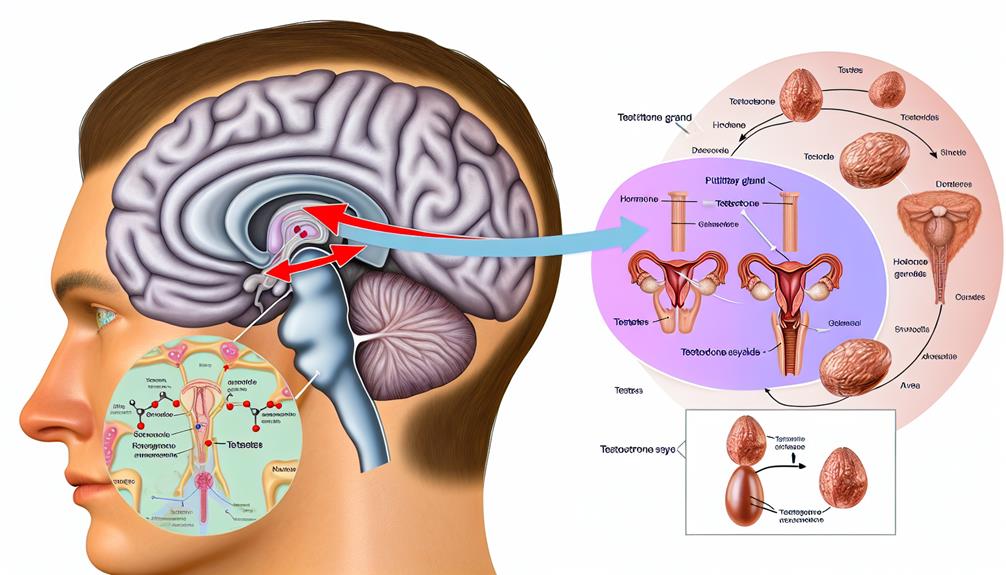
In the intricate web of hormone regulation, testosterone production primarily hinges on the interplay between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and testes. This process begins with the hypothalamus releasing gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the anterior pituitary gland. In response, the pituitary secretes luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). While FSH plays a role in spermatogenesis, it's LH that directly drives testosterone synthesis in the Leydig cells of the testes.
The endocrine interplay between these glands is vital for maintaining ideal testosterone levels. Upon stimulation by LH, Leydig cells convert cholesterol into testosterone through a series of enzymatic reactions. This process, known as steroidogenesis, involves several key steps, including the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone, which is then transformed into testosterone via intermediates such as progesterone and androstenedione.
Notably, the efficiency of this testosterone production can be influenced by various factors, including age, health status, and environmental impacts. For instance, disruptions in hypothalamic function can lead to reduced GnRH secretion, ultimately affecting LH levels and, consequently, testosterone synthesis. Furthermore, the health of the testes is essential; any impairment can directly hinder testosterone production and affect overall hormonal balance.
Understanding this production process not only highlights the complexity of testosterone synthesis but also emphasizes the importance of the endocrine interplay among the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and testes in regulating male reproductive health.
Feedback Loop Between Glands
Hormonal regulation operates through a complex feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and testes, ensuring stable testosterone levels. This intricate process begins with the hypothalamus, which secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH travels to the pituitary gland, stimulating the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones are essential for the functioning of the testes, where testosterone production occurs.
As testosterone levels rise, this triggers a negative feedback mechanism on both the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus reduces GnRH secretion, while the pituitary gland decreases the release of LH and FSH. This feedback loop is fundamental for maintaining homeostasis within the endocrine system. If testosterone levels drop, the opposite occurs; decreased testosterone leads to increased GnRH production from the hypothalamus, stimulating the pituitary to release more LH and FSH, ultimately boosting testosterone synthesis in the testes.
It's fascinating to observe how the hypothalamic control functions in this loop, ensuring that testosterone levels remain within an ideal range. This balance is crucial for various physiological processes, including reproductive function, muscle mass maintenance, and mood regulation. Understanding this feedback loop not only highlights the interconnectedness of the endocrine system but also underscores the significance of hormonal equilibrium in overall health. Disruptions in this feedback mechanism can lead to significant clinical implications, making it a key area of study within endocrine research.
Factors Affecting Testosterone Levels
In examining testosterone levels, I find it essential to evaluate both hormonal regulation mechanisms and the impact of lifestyle and nutrition. These factors interconnect to influence the production and balance of testosterone in the body. Understanding their roles can provide valuable insights into maintaining ideal testosterone levels.
Hormonal Regulation Mechanisms
How do various factors influence testosterone levels in the body? The regulation of testosterone is a complex interplay of hormonal interactions and endocrine signaling. The pituitary gland plays a pivotal role, releasing luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulate the testes to produce testosterone. However, this process isn't solely dependent on these hormones. External factors such as stress, age, and overall health notably impact hormonal signaling pathways.
For instance, chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can inhibit the secretion of LH, thereby reducing testosterone production. Furthermore, age-related declines in testosterone are linked to changes in endocrine signaling, where the responsiveness of the testes to LH diminishes over time.
Additionally, conditions such as obesity can disrupt normal hormonal interactions, leading to lower testosterone levels due to increased aromatase activity, which converts testosterone to estrogen. This intricate web of factors highlights that maintaining balanced hormone levels requires a thorough understanding of both intrinsic and extrinsic influences. Recognizing these hormonal regulation mechanisms can provide insight into optimizing testosterone levels and overall endocrine health.
Lifestyle and Nutrition Impact
When considering the factors that influence testosterone levels, lifestyle and nutrition emerge as significant components. I've observed that our dietary choices can greatly impact hormone production. A diet rich in healthy fats—such as omega-3 fatty acids—vitamins, and minerals tends to support ideal testosterone levels. Conversely, excessive sugar and processed foods can lead to insulin resistance, which negatively affects hormonal balance.
Moreover, exercise routines play an important role in maintaining testosterone levels. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and resistance training have shown to boost testosterone production effectively. I've found that incorporating regular strength training not only enhances my physical performance but also positively influences my hormonal health. On the flip side, a sedentary lifestyle is linked to lower testosterone levels, emphasizing the importance of movement.
Lastly, managing stress through lifestyle modifications—like mindfulness practices—can also create a favorable environment for testosterone production. Overall, it's clear that being mindful of our dietary choices and exercise routines is essential for maintaining healthy testosterone levels, ultimately contributing to overall wellness and vitality.
Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance can manifest through a variety of symptoms that considerably impact daily life. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for anyone suspecting a hormonal issue, and a symptoms checklist can be a valuable tool. For instance, fluctuations in testosterone levels, mediated by the pituitary gland, can lead to an array of physical and psychological effects.
To illustrate, I've compiled a table that highlights some of the common symptoms associated with hormonal imbalance:
| Symptom | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness despite adequate rest | Reduced productivity and motivation |
| Mood Swings | Sudden changes in emotional state | Difficulty in personal and professional relationships |
| Decreased Libido | Reduced interest in sexual activity | Strain on intimate relationships |
| Muscle Weakness | Noticeable decline in strength and endurance | Limitations in physical activities |
If you're experiencing these symptoms, a thorough hormonal evaluation can provide insight into your hormonal health. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional, who can conduct tests to assess your hormone levels accurately. Understanding the underlying causes of these symptoms can lead to targeted interventions, improving both physical and emotional well-being. Don't overlook the significance of hormonal balance, as it plays a key role in overall health and quality of life.
Impact of Age on Testosterone
As we age, what changes can we expect in our testosterone levels? It's well-documented that there's an age-related decline in testosterone production, typically beginning around the age of 30. After this point, testosterone levels can decrease by approximately 1% per year. This gradual decline can lead to noticeable changes in physical and mental health, including reduced muscle mass, decreased libido, and even mood fluctuations.
Understanding this decline is essential, as it can greatly impact quality of life. The pituitary gland plays a pivotal role in regulating testosterone levels through its production of luteinizing hormone (LH). As we age, changes in pituitary function can further exacerbate the decrease in testosterone, making it important to monitor hormone levels regularly.
For those experiencing symptoms linked to low testosterone, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) may be recommended. This treatment aims to restore hormone levels to a more youthful state, potentially alleviating some of the symptoms associated with aging. However, it's important to approach TRT cautiously, as it's not suitable for everyone, and the potential risks must be carefully weighed against the benefits.
Conditions Related to Pituitary Dysfunction
There are various conditions that can arise from pituitary dysfunction, greatly impacting testosterone production and overall health. One common issue I often encounter is the presence of pituitary tumors, which can disrupt the gland's normal hormonal output. These tumors can lead to decreased testosterone levels, resulting in symptoms like fatigue and reduced libido. It's essential to evaluate genetic factors that might predispose individuals to such endocrine disorders, as they can greatly influence the development and progression of these conditions.
In managing these patients, I rely on a range of diagnostic techniques, including imaging studies like MRI, to identify any structural abnormalities. Once a diagnosis is established, treatment protocols vary based on the severity and underlying cause. Hormonal therapies are often implemented to restore hormonal balance, but I must also evaluate the effects of medications that could alter testosterone levels.
Adrenal involvement is another important aspect; the stress response can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, further complicating patient management. Surgical options may be necessary for patients with considerable tumor burden, providing a potential resolution to hormonal dysfunction.
Ultimately, each case requires a tailored approach, factoring in the individual's unique circumstances and health status. By understanding the interplay between pituitary dysfunction and testosterone production, I can better support patients in achieving ideal health outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes for Balance

Achieving hormonal balance often involves implementing targeted lifestyle changes that can greatly impact overall health. I've found that establishing a well-structured exercise routine is essential. Regular physical activity not only enhances testosterone levels but also improves mood and energy levels. Combining aerobic and resistance training can yield ideal results.
Sleep quality cannot be overstated in this equation. Inadequate sleep disrupts hormonal production, particularly testosterone. I prioritize maintaining a consistent sleep schedule to guarantee restorative sleep, which is critical for hormonal balance. Stress management also plays a significant role; chronic stress elevates cortisol, negatively affecting testosterone levels. Incorporating mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, has proven beneficial for my stress reduction.
Dietary choices directly influence hormonal health. I focus on a balanced diet rich in healthy fats, lean proteins, and fiber, which supports weight management and aids in hormone regulation. Hydration levels are equally important; I make a conscious effort to drink enough water throughout the day, as dehydration can impair overall bodily functions.
Furthermore, I emphasize the importance of social connections in my life. Positive relationships can enhance emotional well-being and contribute to hormonal balance. Finally, I consider supplementation strategies, like vitamin D or zinc, after consulting with a healthcare professional, to support testosterone levels effectively. By integrating these lifestyle changes, I've noticed substantial improvements in my overall health and hormonal balance, proving that small adjustments can lead to significant benefits.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
How can medical treatments and interventions effectively address imbalances in testosterone levels? The management of testosterone deficiencies often requires a multifaceted approach involving hormone therapy and careful evaluation of underlying causes. For instance, pituitary tumors may disrupt normal hormonal signaling, necessitating surgical or pharmacological interventions. In such cases, endocrine disorders can greatly impact testosterone production, and understanding these dynamics is essential for effective treatment.
A cornerstone of treatment is hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which can help restore testosterone levels to physiological ranges. Testosterone supplements can be administered via injections, patches, or gels, according to clinical guidelines and treatment protocols established by endocrinologists. It's important to monitor patients through diagnostic tests to guarantee therapeutic efficacy and safety.
Here's a brief overview of common medical interventions:
| Intervention Type | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Hormone Therapy | Restores testosterone levels | Continuous monitoring is necessary |
| Surgical Intervention | Removes pituitary tumors | Requires follow-up for hormonal balance |
| Patient Education | Informs about risks and benefits | Empowers patient involvement in care |
Patient education plays a significant role in promoting adherence to treatment and understanding potential side effects. By providing thorough education, we can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health. Ultimately, this tailored approach to treatment not only addresses testosterone imbalances but also enhances overall quality of life.
Future Research Directions

As we consider the complexities of testosterone imbalances and the current medical interventions available, it becomes clear that future research directions must focus on enhancing our understanding of the underlying mechanisms involved in testosterone regulation. One promising area for exploration lies in the neuroendocrine interactions between the pituitary gland and other brain regions. Investigating how these interactions influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis could provide insights into the precise hormonal feedback loops that govern testosterone production.
Additionally, we should examine the genetic predispositions that may contribute to testosterone imbalances. Identifying specific genetic markers associated with variations in testosterone levels could lead to personalized treatment options, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Understanding how genetic factors interact with environmental influences will be pivotal in developing thorough models of testosterone regulation.
Another avenue worth pursuing is the role of lifestyle factors—such as diet, exercise, and stress—in modulating testosterone levels. Integrating findings from behavioral science with endocrinology could yield a multifaceted approach to treatment that considers both physiological and psychological dimensions.
Lastly, longitudinal studies examining the effects of age on testosterone levels and pituitary function will be essential. By tracking these changes over time, we can better predict and manage testosterone-related conditions in diverse populations. To summarize, the future of testosterone research must embrace a multidisciplinary approach, integrating neuroendocrine interactions, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle factors to enhance our understanding and treatment of testosterone imbalances.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Stress Levels Influence Pituitary Function and Testosterone?
When I consider how stress levels influence pituitary function and testosterone, it's clear that the stress response can disrupt hormonal balance. Chronic stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, leading to elevated cortisol levels. This process can inhibit the pituitary gland's ability to produce hormones like luteinizing hormone, which is vital for testosterone production. Fundamentally, prolonged stress can create a cascade effect, ultimately diminishing testosterone levels and disrupting overall hormonal harmony.
Can Diet Impact Pituitary Gland Health and Testosterone Production?
I believe diet can greatly impact pituitary gland health and testosterone production. For instance, incorporating healthy dietary fats is imperative for hormone synthesis. Furthermore, nutrient timing—fueling my body around workouts—can optimize hormone release. I've noticed that vitamin deficiencies can lead to diminished pituitary function, so addressing those is essential. Finally, maintaining proper hydration status is critical, as dehydration can impair overall endocrine function, including the pituitary's role in testosterone production.
What Role Does Sleep Play in Testosterone Regulation?
Imagine a finely tuned orchestra; each instrument relies on the others for harmony. Sleep quality acts as the conductor, guiding our body's hormonal balance. When I've skimped on sleep, I've noticed my energy dips, and studies show poor sleep can lower testosterone levels. It's like a missing violin; the whole performance suffers. Prioritizing restful sleep can help regulate testosterone, ensuring our body's symphony plays beautifully. So, don't underestimate the power of a good night's sleep!
Are There Specific Supplements That Support Pituitary and Testosterone Health?
I've explored various supplement types that might support pituitary and testosterone health. Natural boosters like ashwagandha and fenugreek are often highlighted for their potential to enhance hormone levels. Additionally, zinc and vitamin D can play vital roles in optimizing testosterone production. It's important to approach these supplements analytically, making sure they align with my health needs. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new regimen to guarantee safety and efficacy.
How Does Physical Activity Affect the Connection Between the Pituitary and Testosterone?
I've found that physical activity greatly influences hormone balance, particularly with exercise intensity. Engaging in moderate to high-intensity workouts can stimulate the pituitary gland, promoting testosterone production. However, excessive or prolonged exercise may lead to a decline in testosterone levels due to stress on the body. It's essential to strike a balance in workout intensity to support ideal hormonal health, ensuring the pituitary gland functions effectively in this intricate system.
