I've found that pituitary gland dysfunction can critically impact male hormones, primarily by disrupting testosterone production. This gland, often called the "master gland," regulates essential hormones like LH and FSH, which are fundamental for triggering testosterone synthesis. When these signals falter, men may experience reduced testosterone levels, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, decreased libido, and mood disturbances. Additionally, the dysfunction can hinder sperm production, increasing fertility issues. It's important to recognize these hormonal imbalances, as they can greatly affect overall health. Exploring further can provide deeper insights into diagnosis and management options.
Understanding the Pituitary Gland
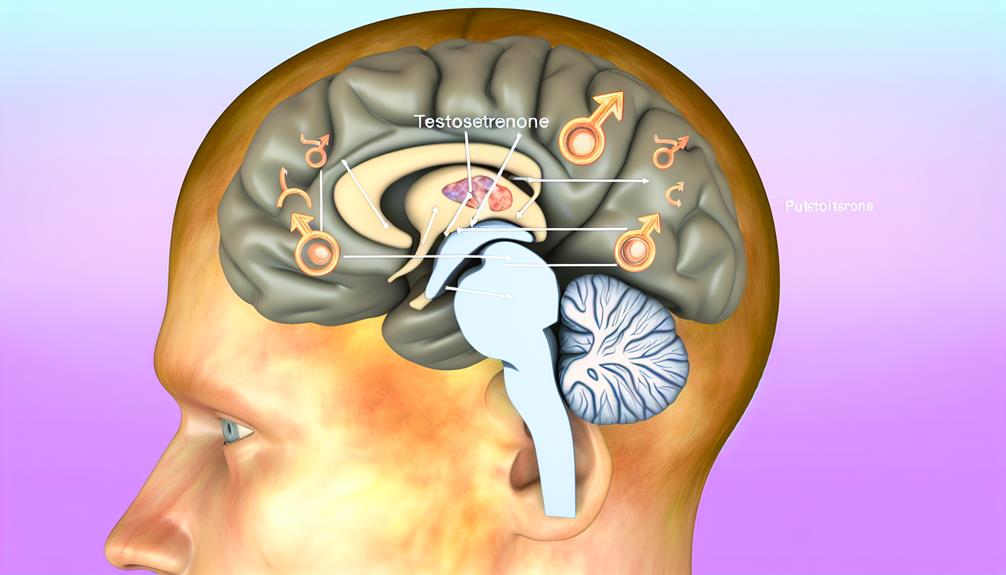
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the "master gland," plays an essential role in regulating various hormonal functions within the body. Nestled beneath the brain and connected to the hypothalamus, its unique pituitary anatomy comprises two distinct lobes: the anterior and the posterior. Each lobe has its specific functions, where the anterior lobe secretes significant hormones such as growth hormone, prolactin, and adrenocorticotropic hormone, while the posterior lobe releases oxytocin and vasopressin.
Understanding the hormonal feedback mechanisms that govern the pituitary gland is critical for grasping its significance in endocrine regulation. The hypothalamus sends signals in the form of releasing hormones to the anterior lobe, prompting it to produce and release its hormones into the bloodstream. This creates a feedback loop, where the levels of hormones in the bloodstream influence the hypothalamus's activity, ensuring a balance is maintained.
For instance, if testosterone levels drop, the hypothalamus will increase its release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), stimulating the pituitary to produce luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which then act on the testes to increase testosterone production. Disruptions in this feedback loop can lead to various hormonal imbalances, affecting male health. As a result, a thorough understanding of the pituitary anatomy and hormonal feedback mechanisms is essential for identifying potential dysfunctions and their implications on male hormones.
Role of Hormones in Male Health
While understanding the role of hormones in male health can be complex, it's essential to recognize that testosterone, alongside other hormones like LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone), fundamentally influences various physiological processes. These hormones are critical in maintaining hormonal balance, which is essential for optimal male vitality. Testosterone is primarily responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, influencing muscle mass, bone density, and fat distribution.
LH and FSH, produced by the pituitary gland, regulate testosterone production in the testes and support spermatogenesis, respectively. The interplay between these hormones guarantees that testosterone levels are maintained within a healthy range, which is crucial for reproductive health and overall well-being. When there's an imbalance, it can lead to significant health issues, such as diminished libido, fatigue, and mood disturbances.
Moreover, hormonal balance extends beyond just testosterone. Other hormones, like estrogen and cortisol, also play roles in male health, affecting everything from mood to metabolism. If the pituitary gland does not function properly, it can disrupt the entire endocrine system, leading to a cascade of hormonal imbalances that can compromise male vitality.
Common Symptoms of Dysfunction
Hormonal imbalances stemming from pituitary gland dysfunction can manifest in a variety of ways, impacting both physical and mental health. When I look at the common symptoms, I realize they're not just limited to one aspect of life; they affect multiple dimensions. Physically, I might notice fatigue, reduced libido, or unexpected weight changes, which can considerably alter my daily activities. These symptoms can stem from fluctuations in hormones that the pituitary gland regulates, such as luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Mentally, the effects can be equally profound. Mood swings, increased anxiety, or even depression can arise as a direct result of hormonal imbalance. I've observed that lifestyle factors, including diet and exercise, play a key role in exacerbating these symptoms. Poor nutrition or lack of physical activity can intensify feelings of fatigue and mood disturbances.
It's essential to reflect on stress management techniques, too. Chronic stress can further complicate the situation, as it may lead to an overproduction of cortisol, which directly influences hormone levels. I've found that implementing strategies like mindfulness, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help mitigate some of these symptoms.
Impact on Testosterone Levels
In examining the impact of pituitary gland dysfunction, I find that the disruption of hormonal regulation can markedly lower testosterone levels. This reduction often manifests in various symptoms, which can affect overall health and quality of life. Understanding these symptoms and exploring available treatment options is essential for effective management.
Hormonal Regulation Disruption
Over time, disruptions in the pituitary gland can greatly impact testosterone levels, leading to various physiological and psychological effects. The pituitary gland plays a critical role in hormonal feedback mechanisms that regulate testosterone production. When this gland is dysfunctional, it can alter the delicate endocrine balance, causing a significant decline in testosterone synthesis.
The pituitary secretes luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), both necessary for stimulating testosterone production in the testes. A malfunctioning pituitary may produce inadequate amounts of these hormones, resulting in insufficient stimulation of the Leydig cells. Consequently, testosterone levels drop, disrupting the body's hormonal feedback loop.
This imbalance can affect not only testosterone but also other hormones, compounding the issue and potentially leading to a cycle of hormonal dysregulation. The interplay between the pituitary, hypothalamus, and testes is essential for maintaining ideal testosterone levels. Disruption in any part of this axis can lead to significant hormonal instability, highlighting the importance of the pituitary gland in regulating male hormones. Understanding these dynamics is key for addressing the broader implications of pituitary dysfunction on male health.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
The consequences of low testosterone can manifest in various ways, notably impacting an individual's quality of life. As I've observed, symptoms often range from physical changes to emotional disturbances, which can greatly disrupt hormonal balance.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness affecting daily activities. |
| Decreased Libido | Noticeable drop in sexual desire, impacting relationships. |
| Mood Changes | Increased irritability or depression, affecting emotional well-being. |
In my experience, these symptoms can lead to a downward spiral, where low energy levels hinder motivation, and diminished libido strains interpersonal connections. It's vital to recognize that testosterone therapy may be a necessary intervention for those experiencing these symptoms. This therapy aims to restore hormonal balance, alleviating the adverse effects of low testosterone.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Early identification and intervention can greatly improve quality of life and overall well-being. Remember, understanding the effects of low testosterone is the first step toward addressing them effectively.
Treatment Options Available
Addressing low testosterone levels often necessitates exploring various treatment options tailored to individual needs. In my experience, the first step usually involves lifestyle modifications. Implementing a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep can markedly influence hormone levels. For instance, resistance training has been shown to boost testosterone production, while reducing body fat can improve overall hormonal balance.
If lifestyle changes aren't sufficient, I often consider alternative therapies. Herbal supplements, such as fenugreek or ashwagandha, may provide some benefits, although their efficacy can vary among individuals. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any alternative therapy, as interactions with existing medications can pose risks.
For more severe cases, hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) might be appropriate. This involves administering testosterone through injections, patches, or gels. While HRT can effectively restore testosterone levels, it requires careful monitoring to avoid potential side effects, including cardiovascular risks.
Ultimately, the ideal treatment plan should be personalized, considering both the physiological and psychological aspects of low testosterone, ensuring an all-encompassing approach to restore balance and improve overall well-being.
Effects on Sperm Production
How does pituitary gland dysfunction impact sperm production? When the pituitary gland fails to function effectively, it disrupts the hormonal signals essential for sperm production. This gland plays a fundamental role in regulating the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), both critical for testosterone synthesis and spermatogenesis. A deficiency in these hormones can lead to reduced testosterone levels, considerably impairing sperm quality and ultimately resulting in fertility issues.
I've observed that men with pituitary dysfunction often experience a decline in their sperm count and motility, markers that are important for effective reproduction. The connection between hormone levels and sperm quality is well-established: lower testosterone impairs the development of sperm cells in the testes. Additionally, inadequate FSH levels can hinder the maturation process of these cells, leading to abnormal sperm morphology.
In my analysis, it's clear that the implications extend beyond just a reduction in quantity. Fertility issues stemming from pituitary gland dysfunction can manifest in various ways, from difficulty conceiving to increased rates of miscarriage. The overall health of sperm—its ability to fertilize an egg and sustain a pregnancy—becomes compromised. Therefore, understanding the intricate relationship between the pituitary gland and sperm production is essential for addressing male fertility challenges. By acknowledging these effects, we can better navigate the complexities of reproductive health in the context of hormonal imbalances.
Causes of Pituitary Dysfunction
In exploring the causes of pituitary dysfunction, I find it essential to contemplate several key factors. Genetic disorders can greatly impact the gland's function, while tumors may disrupt hormone secretion. Additionally, inflammatory conditions can further compromise pituitary health, leading to a cascade of hormonal imbalances.
Genetic Disorders Impacting Function
Genetic disorders can severely compromise the intricate functioning of the pituitary gland, leading to a cascade of hormonal imbalances. I've observed that specific genetic mutations can disrupt the development and functionality of the gland, resulting in considerable endocrine issues. For instance, mutations in the PROP1 gene are known to cause combined pituitary hormone deficiencies, manifesting as growth hormone deficiency, adrenal insufficiency, and hypothyroidism.
Additionally, certain hereditary syndromes, such as Kallmann syndrome, impact the pituitary's ability to produce critical hormones. This syndrome is characterized by hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to a lack of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, which ultimately leads to insufficient testosterone production in males.
Moreover, conditions like Turner syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome are also linked to pituitary dysfunction, stemming from chromosomal abnormalities that affect hormone regulation. These genetic factors highlight the complex interplay between genetics and hormonal health. Understanding these genetic disorders is essential for diagnosing and managing pituitary dysfunction, as timely intervention can considerably improve outcomes and restore hormonal balance.
Tumors Affecting Hormone Secretion
While genetic disorders present notable challenges to pituitary gland function, tumors also play a fundamental role in hormone secretion abnormalities. In my investigation of pituitary dysfunction, I've found that pituitary adenomas, which are benign tumors, can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones produced by the gland. These adenomas might secrete excess hormones or inhibit the production of others, leading to a hormone imbalance that can have profound effects on male health.
For instance, an adenoma secreting prolactin can cause decreased testosterone levels, resulting in symptoms like reduced libido and fertility issues. Conversely, growth hormone-secreting adenomas can lead to acromegaly, impacting overall metabolic function and physical appearance. The severity of these hormone imbalances often hinges on the tumor's size and its specific hormone secretion profile.
Furthermore, the presence of a tumor can create pressure on surrounding structures, potentially impairing the gland's ability to function normally. As I probe deeper into this topic, it becomes evident that understanding the implications of pituitary adenomas is essential for diagnosing and managing hormone-related disorders effectively. Addressing these tumors can greatly improve hormonal balance and, ultimately, overall health.
Inflammatory Conditions and Pituitary
How do inflammatory conditions contribute to pituitary dysfunction? I find that both autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammation play significant roles in disrupting pituitary gland function. Autoimmune diseases, such as lymphocytic hypophysitis, occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the pituitary tissue. This can lead to inflammation and damage, impairing hormone production and secretion.
Chronic inflammation, often resulting from conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or chronic infections, can also negatively impact the pituitary gland. The inflammatory cytokines released during these processes can interfere with the normal signaling pathways that regulate pituitary function. Over time, this can lead to hypopituitarism, a condition characterized by decreased hormone levels that profoundly affect male health.
Moreover, the interplay between chronic inflammation and hormonal pathways is complex. Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines can lead to altered feedback mechanisms, affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Consequently, this may result in diminished testosterone levels and other hormonal imbalances, which are critical for male reproductive health. Recognizing these inflammatory conditions as potential causes of pituitary dysfunction is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies.
Diagnosis and Testing Methods
Accurate diagnosis of pituitary gland dysfunction is essential for effective treatment of male hormone imbalances. To begin, I gather a detailed patient history, which often reveals critical information regarding symptoms and onset. Following this, I conduct thorough physical examinations to assess for any notable signs of hormonal imbalance.
Blood tests are the next step; they allow me to measure levels of various hormones, including testosterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormone assays provide significant data to determine if the pituitary gland is functioning properly. If abnormalities are detected, I may consider further diagnostic methods.
Imaging techniques, such as MRI or CT scans, are invaluable in visualizing the pituitary gland structure. These imaging studies help identify any tumors, cysts, or structural anomalies that could be contributing to dysfunction. In some cases, pituitary biopsies may be necessary to obtain tissue samples for pathological evaluation.
If the findings suggest a complex endocrine disorder, I often make endocrine referrals for specialized evaluations. These specialists can perform more targeted assessments and tests that may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Ultimately, a combination of clinical evaluations, blood tests, imaging techniques, and, when warranted, biopsy results, allows me to form a thorough understanding of the patient's condition. This detailed approach guarantees that we can accurately diagnose pituitary dysfunction and address the resulting male hormone imbalances effectively.
Treatment Options Available
Exploring treatment options for pituitary gland dysfunction is essential in addressing male hormone imbalances effectively. When tackling these imbalances, a multifaceted approach is often necessary, combining lifestyle modifications with pharmacological therapies tailored to individual needs.
First, I find that lifestyle modifications can considerably support overall hormonal health. These adjustments might include:
- Regular exercise to boost testosterone levels
- A balanced diet rich in healthy fats and proteins
- Adequate sleep to enhance hormone regulation
- Stress management techniques, like mindfulness or yoga
- Avoiding alcohol and smoking to prevent further hormonal disruption
In parallel, pharmacological therapies play a key role in managing hormonal deficiencies or excesses. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is frequently prescribed to restore testosterone levels, depending on the specific dysfunction. Additionally, medications such as dopamine agonists may be indicated for conditions like prolactinoma, which can interfere with hormonal balance.
It's important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. Monitoring hormone levels through regular testing guarantees that the chosen interventions are effective and safe. I've learned that addressing the underlying pituitary dysfunction not only helps in restoring hormonal balance but also improves overall quality of life. Ultimately, a thorough approach incorporating both lifestyle changes and medication can lead to considerable improvements in health and well-being for those affected by pituitary gland dysfunction.
Long-term Health Implications
With pituitary gland dysfunction, the long-term health implications can be significant and multifaceted. I've observed that chronic hormonal imbalance often leads to various long-term consequences that can profoundly impact a man's overall health and quality of life. For instance, testosterone deficiency can result in decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and diminished bone density, heightening the risk of osteoporosis.
Moreover, the psychological effects shouldn't be underestimated. Men with untreated pituitary disorders often experience persistent fatigue, depression, and diminished libido, which can exacerbate feelings of inadequacy and affect interpersonal relationships. This emotional strain can further contribute to chronic health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, due to the interplay between stress and hormonal regulation.
Additionally, I've noted that the dysregulation of other pituitary hormones can lead to complications like adrenal insufficiency or hypothyroidism. These conditions can create a cascade of metabolic disturbances, leading to weight gain, insulin resistance, and increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes.
In the long term, the consequences of pituitary gland dysfunction can extend beyond hormonal disturbances, affecting multiple body systems and overall health. Therefore, it's essential for individuals experiencing symptoms of pituitary dysfunction to seek thorough evaluations and tailored treatment plans. Addressing these disturbances early can mitigate the risk of chronic health issues and enhance long-term well-being. Understanding the gravity of these implications allows us to prioritize proactive health management and seek appropriate interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Pituitary Dysfunction Affect Mental Health in Men?
Imagine a delicate orchestra, where each instrument must harmonize to create a symphony; that's how our hormones work. When there's a pituitary dysfunction, it can lead to a hormonal imbalance, causing mood disorders. I've seen firsthand how this disruption can transform vibrant personalities into shadows of their former selves, as anxiety and depression take center stage. Understanding this connection emphasizes the need for addressing hormonal health to restore both balance and emotional well-being.
How Does Age Influence Pituitary Gland Health?
As I've researched, age markedly influences pituitary gland health, often leading to hormonal changes. I've found that, with age, there's an age-related decline in pituitary function, which can affect hormone production and regulation. This decline can result in decreased levels of critical hormones, impacting various bodily functions. Understanding this relationship helps me appreciate the importance of monitoring pituitary health as we age, ensuring we address any emerging issues proactively.
Are There Lifestyle Changes That Support Pituitary Function?
As the saying goes, "an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure." I've found that making lifestyle changes can markedly support pituitary function. Dietary adjustments, like increasing whole foods, are essential. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, help maintain hormone balance. Regular exercise routines boost overall health, while prioritizing sleep hygiene guarantees restorative rest. Additionally, nutritional support through vitamins and minerals plays a significant role in maintaining ideal pituitary performance.
Can Medications Impact Pituitary Gland Performance?
Absolutely, medications can impact pituitary gland performance considerably. For instance, certain medication types, like corticosteroids, can alter hormone levels, affecting the gland's function. Additionally, hormone therapy might be prescribed to address deficiencies, but it's essential to monitor its effects carefully. I've seen how adjustments in medication can lead to changes in hormone balance, which emphasizes the need for a tailored approach to treatment that considers both the medication and the individual's condition.
Is Pituitary Dysfunction Hereditary or Genetic?
When I dive deep into the question of whether pituitary dysfunction is hereditary or genetic, I can't help but feel overwhelmed by the complexities involved. It's not just a simple yes or no; genetic factors play a significant role, and certain hereditary conditions can predispose individuals to dysfunctions. While I'm fascinated by how these elements intertwine, the reality is that genetics can influence various health outcomes in ways we're still unraveling.








